What is an arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is an abnormal rhythm of the heart, which can cause the heart to pump less effectively. It most often occurs in adults but can also occur in children. Some arrhythmias are not dangerous, while others can be life threatening.
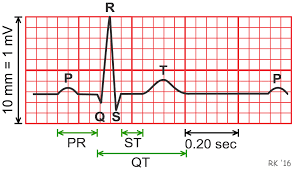
Arrhythmias are classified by the area of the heart where they start: the upper chambers (atria) or lower chambers (ventricles). They can be related to the heart beating too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia) or in an irregular pattern (fibrillation).
There are many types of arrhythmias, including:
atrial flutter
atrial fibrillation
sinus arrhythmia
sinus tachycardia
sick sinus syndrome
premature supraventricular contractions or premature atrial contractions (PAC)
supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) or paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT)
premature ventricular contractions
ventricular tachycardia
ventricular fibrillation
What are the symptoms of an arrhythmia?
Some arrhythmias cause no symptoms. When they do, symptoms can include:
fatigue
rapid breathing
palpitations
dizziness
fainting
What are the causes of an arrhythmia?
Arrhythmias occur when there is a problem with the electrical signals that control the heartbeat. Sometimes the nerve cells that create the electrical signals don’t work the way they should or don’t move normally through the heart. In some cases, other areas of the heart begin to produce electrical signals that disrupt the normal heartbeat.
There is a specific Electrophysiology team with a special interest in complex paediatric rhythm issues. If necessary a referral can be made to one of this team to further investigate and treat these conditions.